When it comes to the general speed of PCs, Solid State Disks, or SSDs for short, are perhaps the most important components. Flash-based data storage devices are usually many times faster when reading and writing data than their electromagnetic predecessors, the classic hard drives in the form of HDDs (Hard Disk Drives). But what about the need for optimization of SSDs? Anyone who has worked with PCs long enough knows that classic hard drives should be defragmented from time to time for optimal operation. But does this also apply to SSDs? We clarify!
Defragment: This is what it's good for
Classic hard disks (“Hard Disk Drives” or “HDDs” for short) become slower and slower over time. This is particularly noticeable when many and above all small files are written to the hard drives over the months and years. The reason for this lies in the physical functionality of HDDs: The data is stored on a turntable over which the hard disk read head is moved - in principle, this process is comparable to a classic vinyl long-playing record. The data saved on the hard drive are arranged in blocks and are saved one after the other by default. In order for a file to be read, the read head must be brought to the appropriate location.
When you save the files for the first time, they are saved “in one piece”. However, over time it happens that deleting individual files creates gaps in the block structure that are later filled with new data. If a new file is larger than the available gap, Windows, Linux and Co. divide it up accordingly into several blocks - this creates what is known as fragmentation. The result: The files are no longer saved in one piece and the magnetic read head can no longer read the data without interruption. Instead, the head bounces back and forth on the surface of the hard drive. Since the hard disk loses some time with the realignment of the read head with every write and read process, the fragmentation makes classic HDDs slower.
If files are no longer saved in one piece, one speaks of fragmentation. With classic magnetic hard drives, this leads to a loss of speed.
The solution for this is defragmentation. The file system can be completely reorganized, as it were, using on-board system resources or specialized software. When this process is completed, the data is available again in one piece, which results in a higher speed, especially when reading..
SSDs: No moving parts, no benefits from defragmentation
Files are also stored in blocks on solid state disks, or SSDs for short - is it advisable to defragment SSDs on a regular basis as well? So much can already be revealed: No, it is not. This is due to the completely different functionality of SSDs. In contrast to classic hard drives, SSDs do not have any mechanical parts. So there is neither a rotating platter nor a reading head that has to be moved back and forth. Instead, the data is stored on solid state disks on flash memory. The controller of the SSD addresses the corresponding memory blocks directly and without electromechanical parts when writing and reading. Put simply, that's why SSDs work so much faster than HDDs. Even more relevant for us:The individual storage cells of SSDs are always reached at the same speed. When reading and writing data on the SSD, it makes no difference whether the data blocks are one behind the other or distributed.
For this very reason, it is not necessary to defragment an SSD - it simply does not bring any advantages. Current operating systems such as Windows 10 or newer Linux versions therefore do not even offer the option of defragmenting SSDs.
That is why defragmentation damages the SSD
Not only does defragmenting SSDs bring no speed benefits, it can even damage the drive! The reason: The memory cells of SSDs have a limited lifespan - after a certain number of write accesses they simply give up the digital ghost. To be fair, it should be said that the risk of dying SSDs is extremely low in practice. The reason for this is on the one hand the now more durable SSD cells, on the other hand also the SSD controllers, which intelligently distribute the storage processes. The controllers ensure that every single storage cell of the solid state disk is used in the same ratio. This means: The controllers distribute the stored data evenly over the SSD surface in order to increase the longevity of the memory.If software - regardless of whether it is an operating system or an external program - intervenes in this process through forced defragmentation, this can lead to a shortened service life..
Optimizing SSD under Windows: useful or not?
Anyone who has already taken a look at the Windows system settings will find that the system also “optimizes” SSDs by default. Just click the " My Computer " or " My Computer " with the right mouse button on the SSD and select " Properties ". In the menu that opens, click on “ Optimize ”. In this window, Windows lists all installed hard drives - regardless of whether they are HDD or SSD. The point “Optimize” is also behind the solid state disks. What exactly is it all about? Well: Unlike with HDDs, Windows automatically recognizes that an SSD defragmentation is not necessary. When optimizing SSDs, which Windows 10 automatically performs once a week, for example, the system checks, among other things, some automatic optimization processes that SSDs offer on the hardware side. One example of this is the correct setting of the so-called TRIM command.
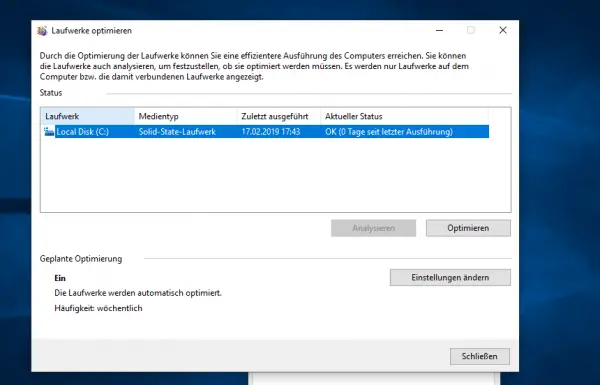
The optimization of SSDs under Windows has nothing to do with the “classic” defragmentation of HDDs.
In short: With a modern operating system, you hardly have to worry about anything when it comes to SSDs. Windows, Linux and macOS have long been optimized for SSD use and themselves ensure that the flash memory functions for a long time and, above all, optimally. So keep your hands off programs that promise advantages by defragmenting SSDs - they simply have no right to exist.