It doesn't always have to be a new card for more graphics performance. Overclocking allows you to tickle more speed out of your existing GPU. We'll show you how to do this and what you need to consider.
What is overclock?
On graphics cards, the computing work is done by the Graphics Processing Unit (GPU). The GPU basically works very similarly to your CPU with a certain clock rate. With an Intel Core i7 CPU this is 1,716 megahertz, for example, with an Nvidia GTX 960 GPU it could be 1,841, for example. And the system memory also works with a rate that specifies arithmetic operations per second. And it is precisely these values that you can increase.
The question arises as to why the manufacturer does not immediately use optimal settings for performance. By default, your graphics card has a setup that ensures safe and stable operation. And higher clock frequencies ensure more power consumption, higher temperatures and overall higher utilization of all hardware . Now these values are kept very conservative for pretty much every card and can handle a little tuning. Overclocking used to be a tricky and not entirely harmless affair for technology nerds, which also ended the warranty. Today, most manufacturers themselves simply supply overclocking tools for the Windows desktop . Nevertheless, be careful announced: Hardware that is overclocked becomes too hot and at some point produces errors. Here you can see that graphics cards not only depend on the best possible Nvidia or Ati GPU, but also on how the manufacturers install cooling and other components.
In addition to the two clock rates, power consumption and ventilation can also be set. You can find more about the individual values in the individual steps for overclocking..
Measure graphics performance
Before doing this, however, it is a good idea to measure the graphics performance and read out values such as clock rates and temperature. With the free GPU-Z you get pretty much all the data about your graphics card that could be of interest, including maximum standard and current clock frequencies. And above all, the " Sensors " tab shows you all the important values in real time: GPU and memory clock, fan speed, temperature, power consumption and voltage. As an alternative to the current value, you can also use the small arrows next to the respective values to display the maximum, minimum and average values . You can save the displayed values as an image using the camera symbol . And you should also do this so that you can check after the tuning measures whether anything has changed at all.
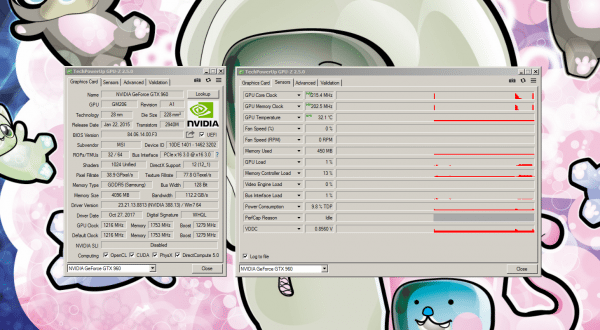 GPU-Z clearly shows the most important sensor data.
GPU-Z clearly shows the most important sensor data. You should also measure the performance in advance . The easiest way to do this is with the free version of 3DMark . The benchmark program plays a whole series of animations in different detail / effect levels and measures the graphics performance. Alternatively, you can of course just start your favorite game and display the displayed images per second (frames per second / FPS)..
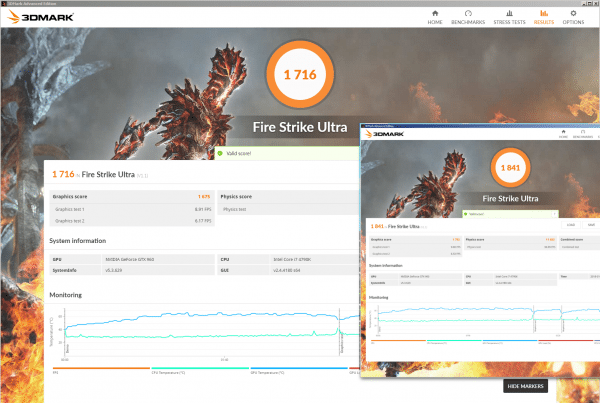
Overclock graphics card
In many cases, you can use the graphics card manufacturer 's tools for overclocking - but of course it looks different every time. But with the MSI Afterburner there is also a wonderfully simple program that not only works with MSI cards, but also with a number of other Nvidia and Ati products.
First of all: If you do not like the display or if it is too confusing, open the settings via the "gear" symbol or the "Settings" button. In the " User Interface " tab you can easily adapt the language and appearance.
 The standard view of the Afterburner is not necessarily clear.
The standard view of the Afterburner is not necessarily clear.
First you can adjust the " Core Voltage (mV) ", that is the applied voltage in millivolts, and the " Power Limit ", that is the maximum current consumption. In particular, you should not touch the voltage without carefully studying your hardware and the effects - this is only useful if you want to push the limits. You do not need the power limit either, if the hardware supports it at all.
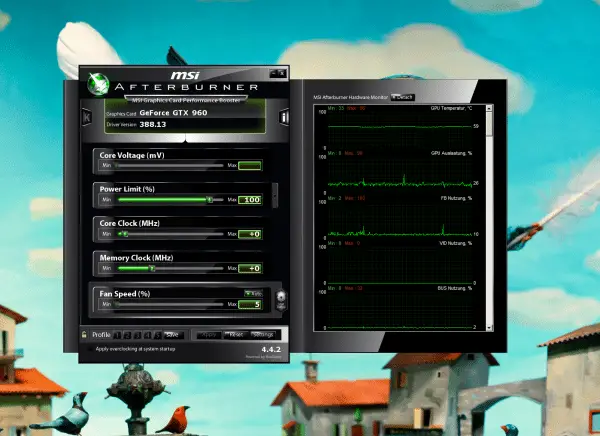 With a more conventional design, Afterburner is a bit clearer.
With a more conventional design, Afterburner is a bit clearer. The values " Core Clock " and " Memory Clock ", ie the clock frequencies of the core and memory, are interesting . Here you should very carefully approach the settings that are still safe . Try it in 5-megahertz steps : increase, apply with the " Apply " button, test the computer in operation. Errors are noticeable , for example, through flickering, artifacts or crashes - if something like this occurs, turn the control back a little! The best thing to do is to take two steps at the same time so as not to keep driving the card to the limit.
Also a look at the temperature Can't hurt, manufacturer limits shouldn't be exceeded. The " Fan Speed " setting can help a little here, by the way, but higher fan speeds also mean more noise and power consumption. Most of the time, the default " Automatic " is perfectly fine. For games or in midsummer it is sometimes worth shifting up.
When you are happy with the settings, you can save them as a profile . So you can quickly switch between maximum performance for gaming and minimum power consumption while surfing. And in case you are wondering what all this brings: A GTX 960 graphics card runs on our test system with a standard 1216 MHz core and 1753 MHz memory clock - these settings achieve 1716 points in the 3DMark benchmark Fire Strike Ultra. With 150 MHz more each time, the test got 1841 points, which is 7.2 percent more. A further increase leads to crashes of the benchmark and incorrect information in GPU-Z.