If only Ubuntu is running on a computer, the deinstallation is done very quickly. It takes a little more effort on a dual-boot computer with Windows and Ubuntu, since the GRUB boot manager has to be removed. We show you both ways here step by step.
Uninstall only Ubuntu
The simplest case: you only have one operating system installed and want to reset the computer for a sale. It gets a little easier if you want to use the computer with a different operating system. Then you can do without "deinstallation" at all and simply install the new system. This is also a viable option when it comes to sales. But back to erasing, which you do in two steps: remove partitions, securely erase data .
To partition, start the computer with the Live Linux Parted Magic from a USB data carrier . Here we show you in detail how you work with Parted Magic. Delete after startup With the partition manager GParted, namesake for Parted Magic, you simply put all partitions on the Ubuntu disk, then create a new, single partition and format it . Basically that's enough, but it doesn't hurt to write the whole new partition full once, so that no one can restore old files.
There are a number of options for overwriting, but one is nice and simple and always available, namely the clone / copy tool dd . First of all you need the name of the former Ubuntu hard drive , usually this should be "sda" if only one hard drive is available. If not, you can find it in GParted. Then open a terminal and enter the following command:
dd if = / dev / random of = / dev / sda
The virtual "device" named "random" is used here as an input file (if for input file) and simply supplies endlessly random data . The data carrier "sda" serves as the output file (of for output file). So dd simply writes random data to the hard drive until it is full. And so you can sell the computer or the hard drive without risking old data being recovered..
Uninstall dual boot Ubuntu
With a Windows-Linux dual-boot system, the procedure is slightly different: Here, too, you have to delete the partitions , but you can do this easily under Windows. On the other hand, you can save yourself overwriting, after all, the computer stays with you. To do this, the boot manager has to be removed , which always asks you when the computer starts up whether Windows or Ubuntu should start.
First open the disk management via " Control Panel / Administrative Tools / Computer Management / Disk Management ". Here you will find a neat list of all your hard disks and their partitions. Ubuntu will have created two partitions by default: a large one for the system itself and a small one for temporary storage (swap), which is probably two to four gigabytes in size. You can use Ubuntu - Recognize partitions by the fact that Windows does not list any names or file systems. You can simply delete both with a right-click . You can then convert the new, empty area into a new partition via the context menu . Or better: If Ubuntu is installed on the same hard drive as Windows you can also extend the Windows partition by the space that has become free . This works via the context menu of the Windows partition and the menu item "Extend". By the way: Windows likes to talk about volumes, but means the same here.
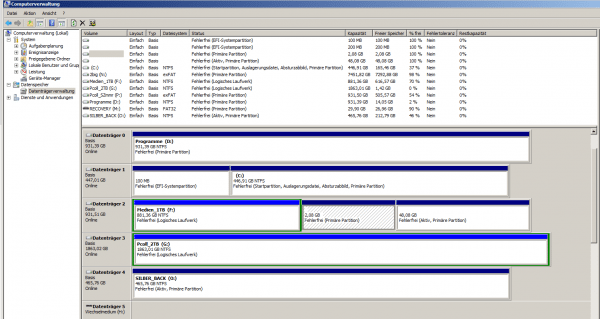 You can find the Linux partitions in Disk Management.
You can find the Linux partitions in Disk Management. Of course, you can also optionally overwrite the newly gained space with random data - better safe than sorry . In Windows this is easy with the free Eraser program. If you have extended the Windows partition: Run in the workplace a right click on the Windows drive and select it from the menu " Eraser / Erase unused space ." With the option Eraser overwrites the entire free space of the partition with a mess of characters and then of course deletes it again. Existing files will of course not be deleted!
Remove boot manager
The easiest way to remove the boot manager is offered by the EasyBCD program. When downloading, you will be redirected to the manufacturer's website. At the bottom you will find a free version for private, non-commercial use in the "Non-commercial free" box. You have to enter a name and an e-mail address via the " Register " button; further information is not required. Fortunately, no activation link or the like is sent to the e-mail address, EasyBCD runs immediately after the download..
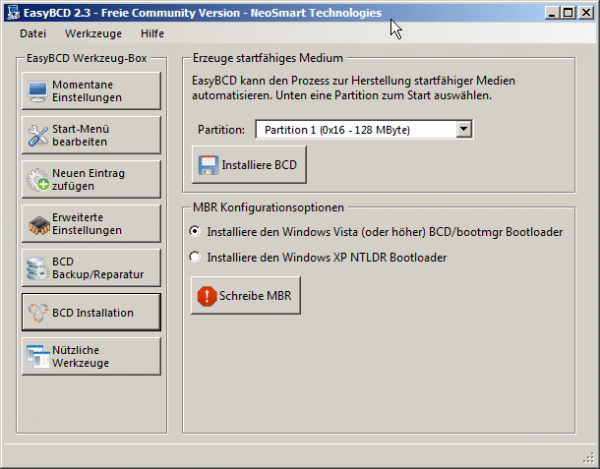 EasyBCD simply completely rewrites the MBR.
EasyBCD simply completely rewrites the MBR.
During the installation you will need to confirm a couple of warning messages and the license . Before you start, I would like to point out again: data loss is unlikely, but it is always possible with such actions. So back up your most important data . In an emergency, it doesn't hurt to have a live Linux on hand so that you can start the computer. In addition, you can also boot Windows via the boot manager on the Live CD if necessary!
So open EasyBCD and switch to the " BCD Installation " tab . Now select your Windows system under " MBR configuration options " - As a rule, "Vista (or higher)" should be the right choice, also with Windows 7, 8 and 10. You only have to switch here if you are actually still using Windows XP.
The " write MBR "-Button then triggers the actual action: MBR stands for Master Boot Record, to put it simply, the beginning of a partitioned data medium that also contains boot managers such as GRUB or Windows' own BOOTMGR. EasyBCD rewrites this area, sets it quasi back. And with that GRUB is gone. Incidentally, in Windows itself you will find the tool "Bcdedit.exe" for the command line, information is available via the command "bcdedit.exe /?". The name of both programs comes from the file , which contains the boot information, the "BCD", which stands for Boot Data Configuration.