If you use the Internet, you come into contact with domains when you visit websites at the latest. But what are domains actually? What is DNS and TLD all about? And what are domains made of? We explain all of this to you in this article.
What is a domain?
A domain is a unique name assigned to a website. The domain of this website is, for example, heise.de .
The domain is part of the Uniform Resource Locator (URL) of a website. A URL is what is colloquially often referred to as "Internet address" or "Link": In addition to the domain as a rough address, it also contains the exact path on the individual website, for example: www.heise.de/tipps-tricks /
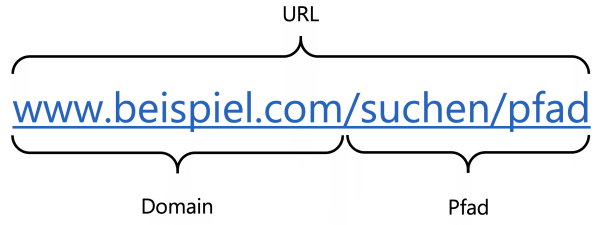
Computers actually reach websites via their IP addresses. These are long strings of numbers and characters that are difficult to remember as an Internet user. This is made much easier by URLs: Your computer first sends an entered URL to a so-called name server, which then looks up the IP address belonging to the domain from the appropriate Domain Name System (DNS) . You can think of DNS as a directory of all existing websites, which stores where you should be forwarded to. Read more about what a URL is here..
What is a domain made of?
A domain usually consists of three levels, each of which refers to a specific part of the Internet when a URL is translated into an IP address.
Please note that domains are evaluated from right to left..
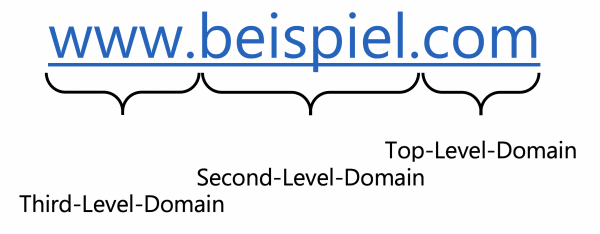
Top-level domain
Top-level domains (TLDs) are often referred to as domain extensions. These include, for example, .com , the country-specific .de and .at or new endings such as. shop . In principle, the TLDs should describe the content of the website - so .com is intended for companies, for example.
A domain name system is maintained for each TLD . The name servers already described exist so that you are forwarded to the correct DNS when a request is made. These ensure that if you want to visit a .com address, you are also forwarded to the DNS that belongs to .com .
Second level domain
The second-level domain is a subdomaine with a freely selectable but unique name that is subordinate to the TLD. Such a second-level domain is always related to the top-level domain and is usually assigned by commercial providers.
Third level domain
Third-level domains are also subdomains, but they are also subordinate to the second-level domain. These can be used to delimit individual areas of your own website from one another: Frequently occurring third-level domains are, for example, www. for websites, m. for websites on mobile devices or abbreviations such as de . or en. for the respective languages.
In addition, further subdomains can be added, but this is less common.
So if you want to call up the website www.example.com , you will first be directed to the DNS for .com addresses by a name server . There to be beispiel.com associated IP address sought out to whom you will be redirected. The sub-address www. indicates in this context that this is a website.