Managing Linux systems involves many tasks, some more important than others, and one of them is precisely having a clear awareness of the size of the directories where we host the files and variables, this is key to knowing the size they occupy on the disk and with it determine debugging tasks in case we have excess unusable space on the computer..
We could go file by file to see their properties and with this determine the size of each one, but this logically becomes a tedious and extensive task, to prevent this Linux offers us the du command for a much more complete control.
Du is a standard Linux command with which we access details and information about disk usage in an integral way, du works integrally for specific directories and has variations that allow us to customize the output according to the information requirements..
getFastAnswer will explain how to use the du command to see the size of a directory in Linux.
To stay up to date, remember to subscribe to our YouTube channel! SUBSCRIBE
How to see the size of a directory in Linux with du
Step 1
The basic syntax is to run du without any parameters, as a result we will see the following:
du
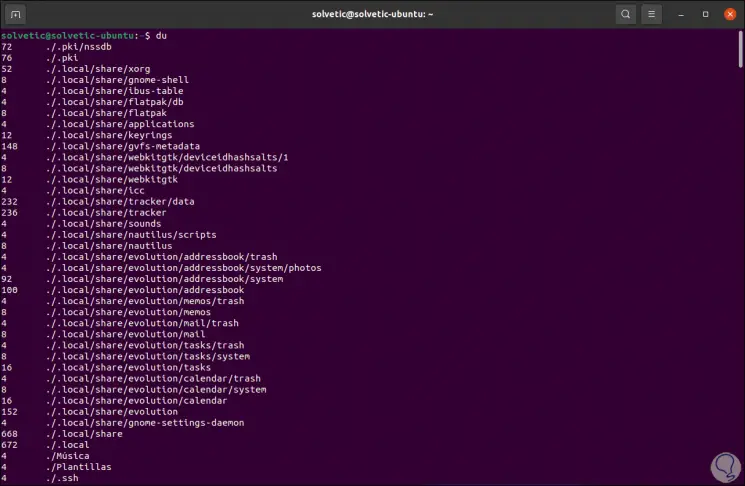
The values that we see on the far left are the disk usage, then we see the specific directory and at the end of the result we find a summary of the entire / home directory..
Step 2
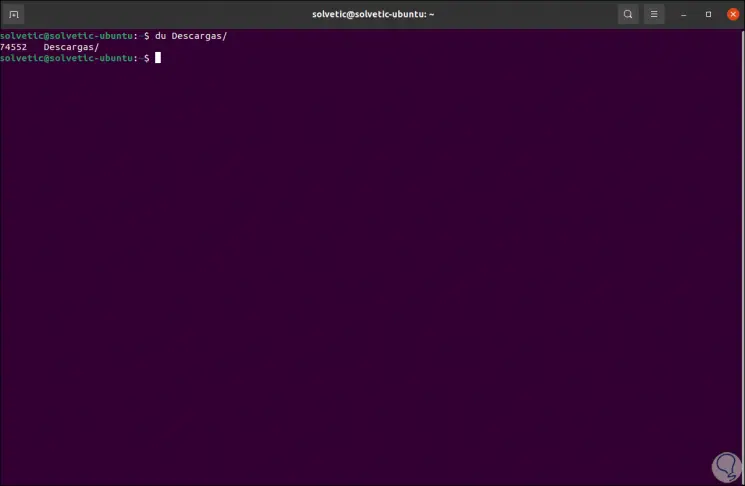
It is possible to use du for a specific directory:
du directory
Step 3
We see that the result is in kilobytes, we can display the size in "human readable format" with the -h parameter:
du directory -h
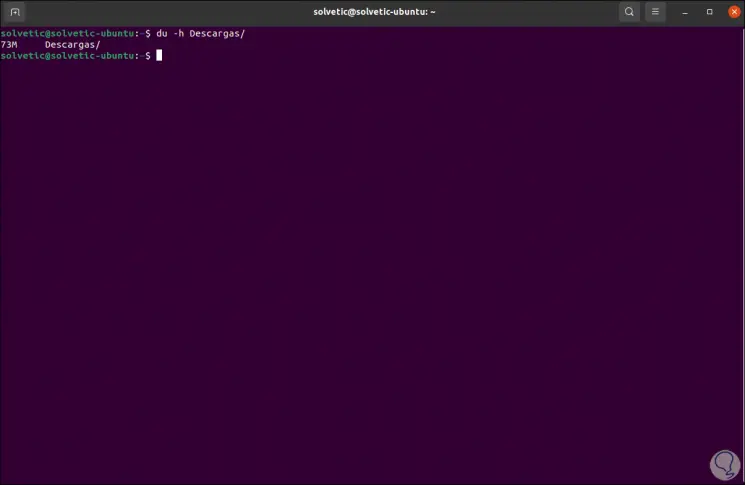
Step 4
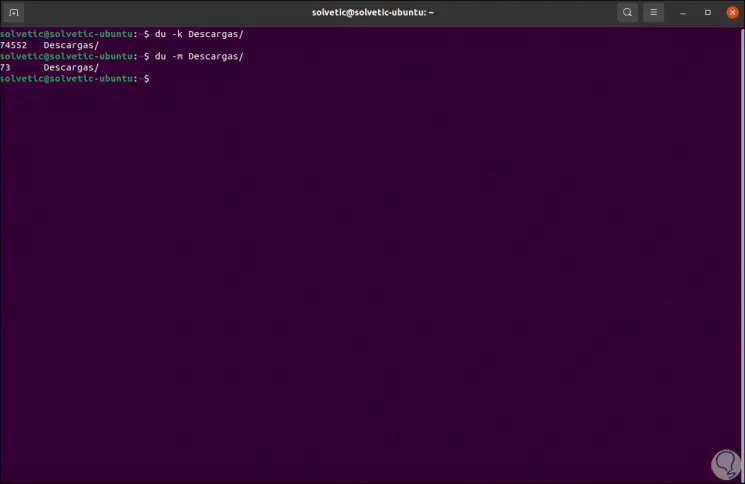
This result is now displayed in MB, this value can be expressed in megabytes or kilobytes as necessary in the following way:
du -k directory / (kilobytes) du -m directory / (megs)
Step 5
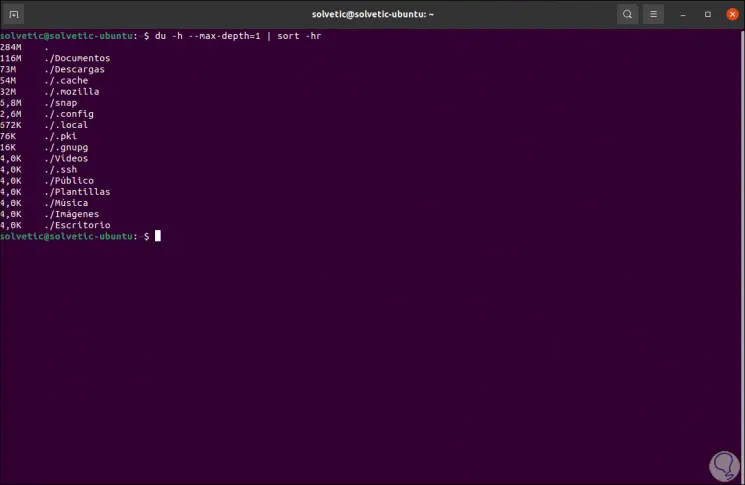
When using the du command, we will see the largest subdirectories at the top, to increase the depth level of the directory, we are going to use the --max-depth parameter as follows:
du -h --max-depth = 1 | sort -hr
Step 6
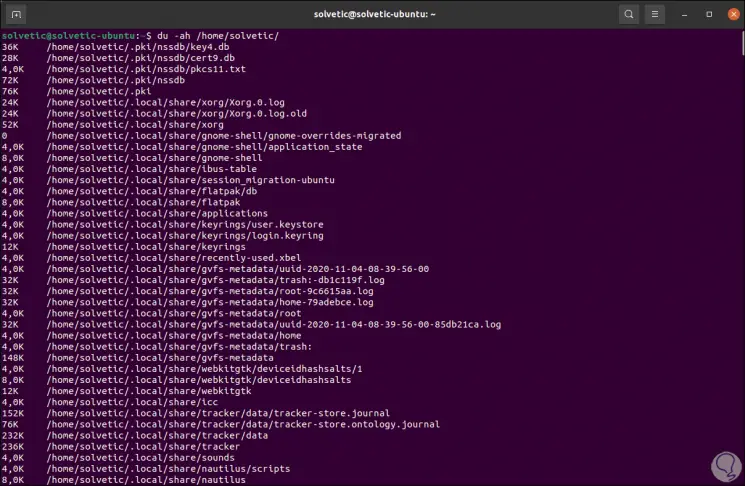
In case we want to display the disk usage of all elements, including files and directories, we will use the -a parameter:
du -ah / directory
Step 7
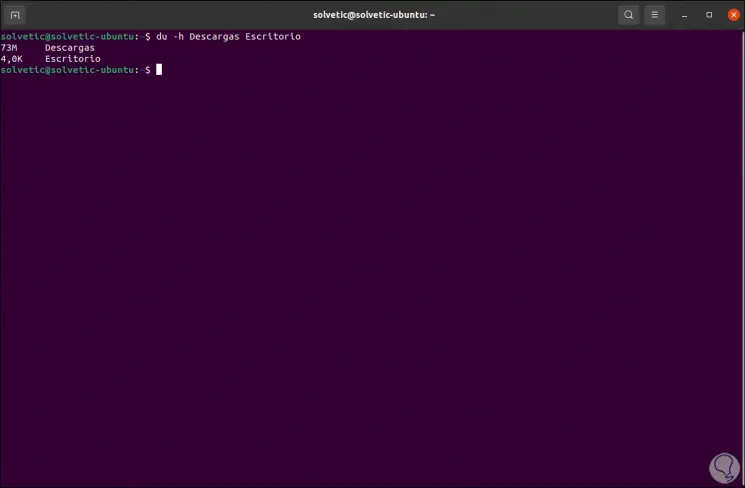
With the du command it is possible to display two or more directories at the same time, for this we execute the following syntax.
du Directory 1 Directory 2
Step 8
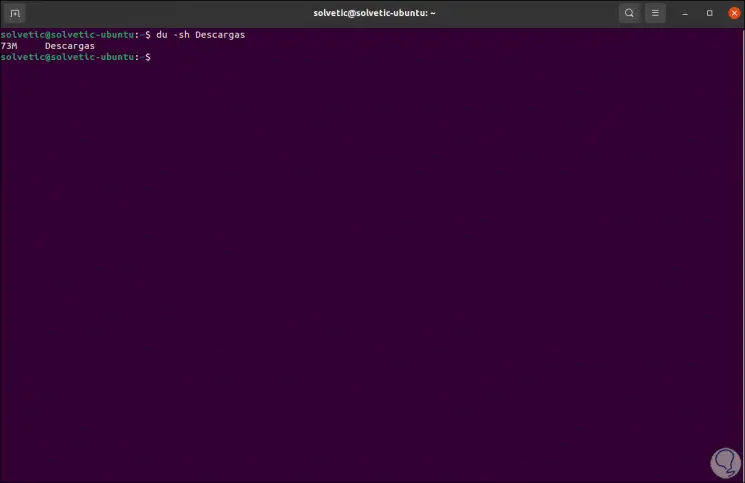
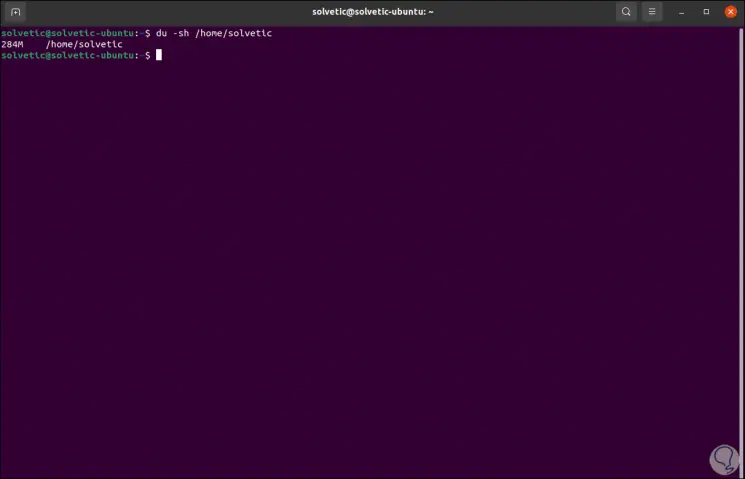
To check the total usage of used disk space for a single directory, we'll use the -s parameter:
du -sh / directory
Step 9
This applies to global directories:
Step 10
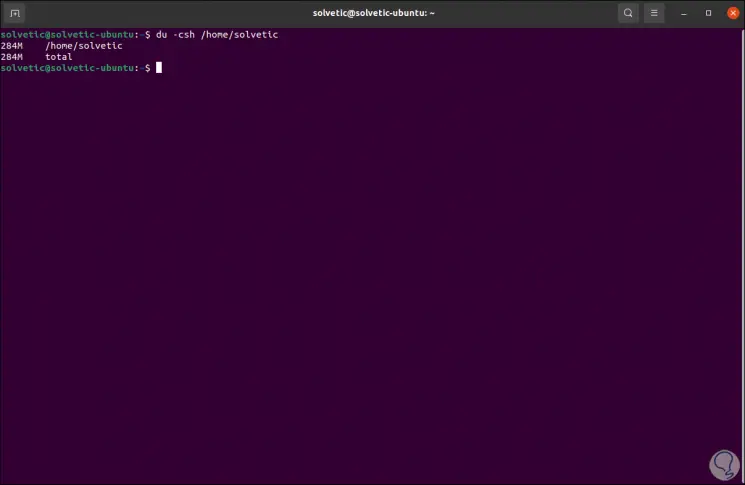
The du command allows us to display global totals thanks to the -c parameter as follows:
du -csh directory
Step 11
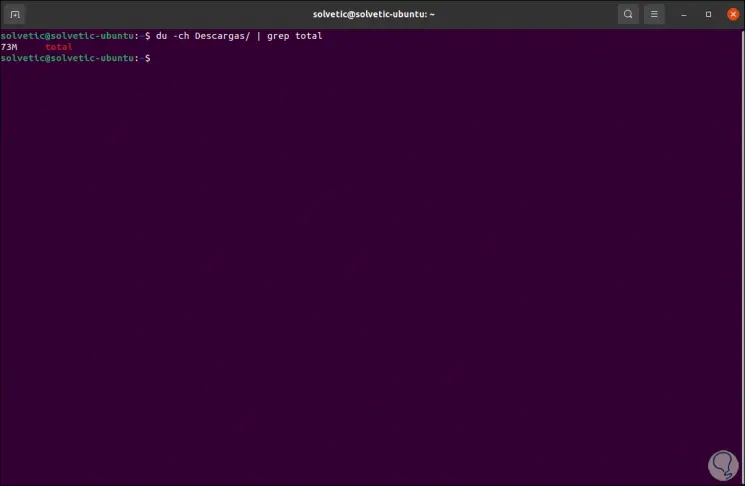
We can only display the general total of the directory including all subdirectories, for this we must use the grep command with the du command like this:
du -ch Downloads / | total grep
Step 12
The general parameters of the du command are:
End each line of output with NULL
Writes the count of all files, not just directories
Print apparent sizes, rather than actual disk usage
Scale sizes to SIZE before printing to console
Generates the grand total of the directory size
Print the total for the directory only if it is N or less levels that are less than the command line argument
Print the result in human-readable format
Applies to directories, in this case it does not include the size of the subdirectories
Shows only the total of each directory
Displays the time of the last modification of any file or directory
With the du command we have at hand a comprehensive solution to know the size of a directory in Linux.