Network administrators who are entrusted with setting up and maintaining a Windows network will sooner or later have to deal with the configuration of a domain controller. The domain controller, also known as the domain controller, is a special server that is responsible for authenticating users on a computer network.
What is a domain controller in Windows?
A domain controller is an essential part of a Windows network domain because the network cannot function without it. Domains are special, independent security areas within a network organization. For example, different locations of a company can each have their own domain. Theoretically, individual departments can also be divided into several domains. In practice, however, it is common practice with Active Directory to set up groups within a domain instead in order to subdivide them further..
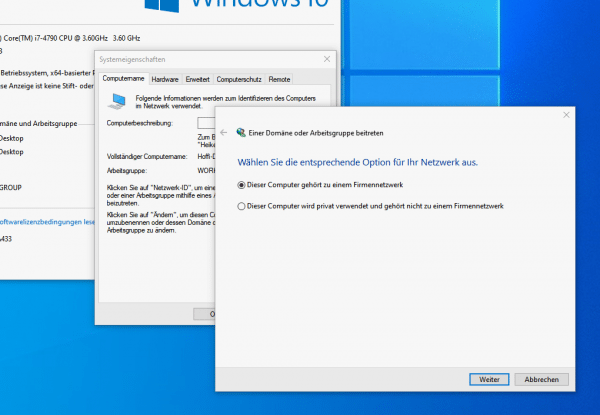 After assigning a user name and password, users can join a domain in the Active Directory network.
After assigning a user name and password, users can join a domain in the Active Directory network. Domain controllers are particularly advantageous in company environments, as each employee can be determined exactly which resources he can access in the network. The security guidelines are also defined on the basis of the domains and, thanks to the domain controller, can be regulated uniformly. The allocation of employees to a domain ultimately determines which data and functions they are allowed to access in the company. When logging in via a domain controller, it doesn't matter which workstation the employees are at - they can log in with their user data on any computer with access to the domain.By assigning users to the different domains, the administrators save themselves having to set up user accounts separately on all workstations in the company. At the same time, domain controllers enable uniform adaptation of all user rights and security guidelines within the network.
Background: Directory services and Microsoft Active Directory
Since the introduction of the Server Edition of Windows 2000, Microsoft has offered a directory service for computer networks in the form of Active Directory. A directory service is an extremely important component in network operating systems. Active Directory is a modernized version of the Windows network functions introduced with Windows NT..
 Windows Server lays the foundation for Active Directory networks based on domain controllers (source: Microsoft.com).
Windows Server lays the foundation for Active Directory networks based on domain controllers (source: Microsoft.com). Directory services such as Active Directory define a namespace for the network. The namespace is used to assign a name, i.e. a unique identifier, to each of the objects. Not only the individual PCs, but also drives, folders, files, printers, users, groups or even telephone numbers serve as network objects.
Directories usually have a set of rules governing how network resources are named and identified, which usually includes a requirement that the identification be unique. In practice, directory services such as Microsoft Active Directory can be compared to a telephone book that provides all important information centrally..
The roles of the domain controller in Active Directory
As already mentioned, in a Windows network the domain controller takes over the authentication of the users and the assignment of the roles. All information in the Active Directory is also stored on the domain controller server. In other words, a domain controller is essentially the heart of a Windows network.
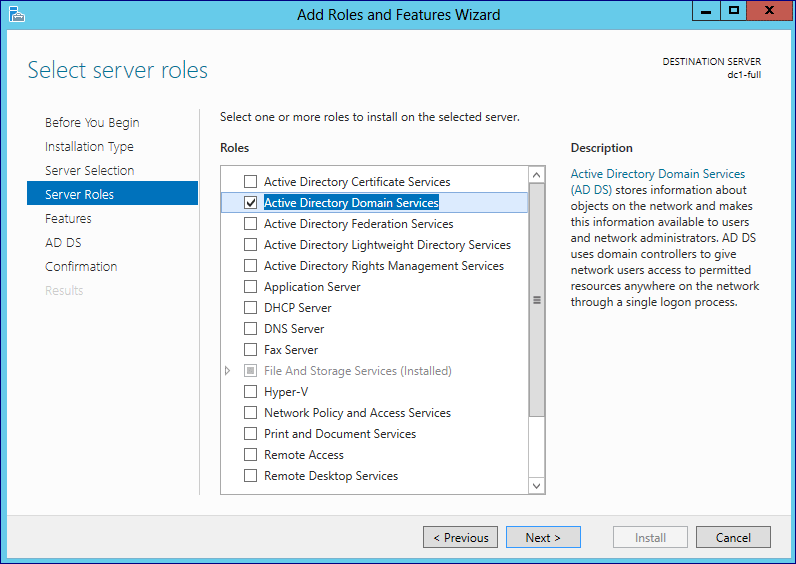 The assignment of roles in a Windows network can be defined in detail for each domain controller under Windows Server (source: Microsoft.com).
The assignment of roles in a Windows network can be defined in detail for each domain controller under Windows Server (source: Microsoft.com). In detail, a domain controller also takes on five other tasks within an Active Directory, the so-called Masters Operations or Flexible Single Master Operations (FSMO). The two roles of schema master and domain naming master are only available once in a network structure with several domains. The infrastructure master, RID master and the PDC emulator, on the other hand, can be assigned to a server once per domain.
By default, all roles are assigned to the first domain controller in a Windows network based on Active Directory. If several servers are used, the administrators can transfer the roles to the different domain controllers.
Microsoft provides an overview of the functions of the individual roles of the domain controller in its online documentation .
Pros and cons of domain controllers
Domain controllers are practically indispensable in companies that store customers or employees in networks. In addition to central user management and the simple, shared use of various resources, domain controllers offer other advantages, such as the encryption of user data.
Due to its prominent function, the domain controller is of course also a typical target for hackers who target the network infrastructure. It is also highly recommended to operate more than one domain controller in parallel. Windows Server offers so-called multimaster replication for this purpose. The function makes it possible to operate several servers as domain controllers on which all information of the Active Directory is stored redundantly. This ensures that network operations can be maintained even if a server fails.