Modern DSL and cable Internet connections are extremely fast: Instead of lazy analog modems or ISDN adapters, as was the case in the past, data is now racing back and forth between PC and Internet at 25, 50, 100 or even more megabits. However, the data transfer sometimes seems to be extremely slow. The provider can be to blame for this, but in most cases there are small things that you can improve yourself. So before you spend hours on the service hotline of your Internet provider, you should make better use of the time - and lend a hand yourself.
Is it the wifi?
One of the most common reasons for a slow Internet connection is the wireless network in your home, your WLAN: This is often slowed down by all sorts of factors. You can test this with a few simple steps:
1st step:
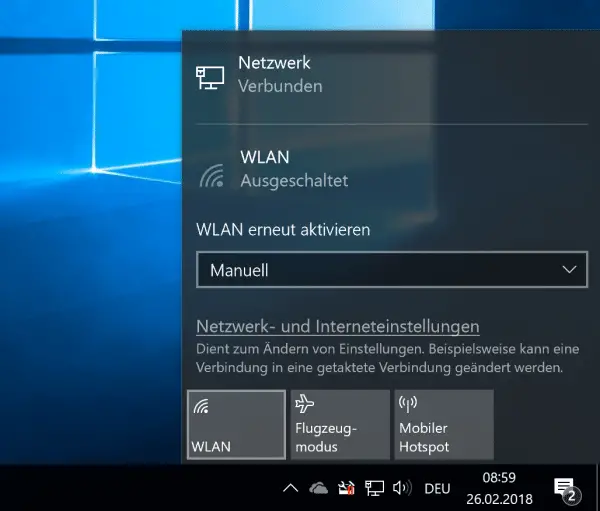 Check with a cable connection between the Internet router and PC / laptop whether the cause is the WLAN connection at all. To do this, first switch off WLAN on the computer.
Check with a cable connection between the Internet router and PC / laptop whether the cause is the WLAN connection at all. To do this, first switch off WLAN on the computer. 2nd step:
 Now connect the computer to one of the suitable ports on the router using an Ethernet cable .
Now connect the computer to one of the suitable ports on the router using an Ethernet cable . 3rd step:
 Go to some websites . Is the internet faster now? Then the slow internet is due to your WiFi connection and you need to improve it. Otherwise you have to optimize something in the router (see instructions below). You can then disconnect the cable connection and turn the WLAN back on .
Go to some websites . Is the internet faster now? Then the slow internet is due to your WiFi connection and you need to improve it. Otherwise you have to optimize something in the router (see instructions below). You can then disconnect the cable connection and turn the WLAN back on . Improve WiFi connection: Here's how
There are several ways to improve your WiFi connection. First of all, you should eliminate interference factors in order to get a better WiFi connection.
1. Disturbance factor: distance
How far is the WLAN router from your PC or notebook? Often the range is simply not sufficient. Try to keep the distance between routers and computers as small as possible..
2. Disruptive factor: water
The same problem exists with water as with distance: water slows down WLAN waves. Slow WiFi can therefore be caused by anything between the router and PC that contains a lot of moisture: concrete walls, plants, high humidity, other people and so on.
3. Disturbing factor: other WLANs and devices
Another source of WLAN interference that should not be disregarded are other devices: Do you use an older Bluetooth mouse or a cell phone next to your computer? Are there many WiFi networks in the area? Try to eliminate as many radio sources as possible..
4. Disruptive factor: WLAN repeater
Last but not least, an often forgotten disruptive factor: WLAN repeater. They promise more range, but cut the speed of the connection in half for technical reasons: Each repeater effectively halves the network speed. Try it once without a repeater.
Internet still slow? Get maximum WiFi performance.
If the WiFi is still slow, you should take a look at the router settings. If you have a modern router, you should set it to "automatic" for maximum performance.
1st step:
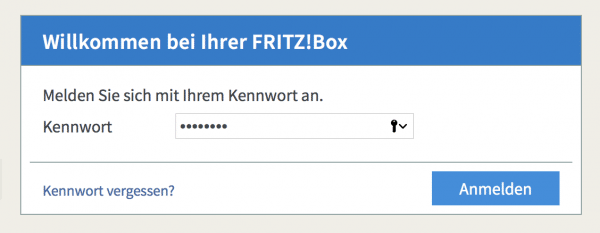 Go to your router user interface . On the FritzBox, log in to the router using http://fritz.box in the browser with your password.
Go to your router user interface . On the FritzBox, log in to the router using http://fritz.box in the browser with your password. 2nd step:
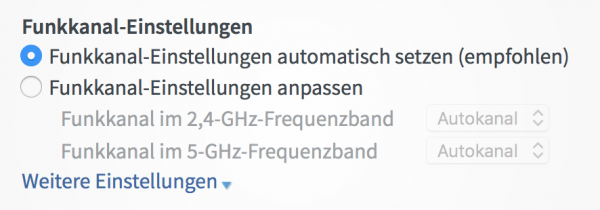 Open the WiFi menu . On the FritzBox the sub-item is called "WLAN -> radio channel". Set the WLAN settings to "Set radio channel settings automatically ". Click Apply to use the automatic settings. The router is now transmitting at maximum power.
Open the WiFi menu . On the FritzBox the sub-item is called "WLAN -> radio channel". Set the WLAN settings to "Set radio channel settings automatically ". Click Apply to use the automatic settings. The router is now transmitting at maximum power. Internet still slow? Separate frequency bands.
If that doesn't have a positive effect, separating the WiFi frequency bands can help. Modern routers usually support dual band: They transmit at 2.4 and 5 gigahertz. The 2.4 GHz network goes further, the 5 GHz network is less prone to interference. If you separate these networks, you have two WLANs: one for “wide” (for example on the balcony) and one for “fast” (for example in the living room near the router).
1st step:
 Open the router settings and select " WLAN -> radio channel " again. Instead of “Set radio channel settings automatically”, select the item “ Adjust radio channel settings ”. Then click on “ Additional Settings ”.
Open the router settings and select " WLAN -> radio channel " again. Instead of “Set radio channel settings automatically”, select the item “ Adjust radio channel settings ”. Then click on “ Additional Settings ”. 2nd step:
 Check whether the " Maximum transmission power " is set to 100 percent. In addition, set the broadest possible standards for the WLAN standard for 2.4 and 5 GHz . Ideally, the 2.4 GHz network runs on " 802.11n + g + b " and the 5 GHz network on " 802.11n + ac ". Older routers may have different settings here. Then click on " Apply ".
Check whether the " Maximum transmission power " is set to 100 percent. In addition, set the broadest possible standards for the WLAN standard for 2.4 and 5 GHz . Ideally, the 2.4 GHz network runs on " 802.11n + g + b " and the 5 GHz network on " 802.11n + ac ". Older routers may have different settings here. Then click on " Apply ". 3rd step:
 Now switch to the “ WLAN -> Wireless Network ” menu and scroll down a little. Here you will find the options " Name of the WLAN radio network " for the 2.4 and 5 GHz networks.
Now switch to the “ WLAN -> Wireless Network ” menu and scroll down a little. Here you will find the options " Name of the WLAN radio network " for the 2.4 and 5 GHz networks. 4th step:
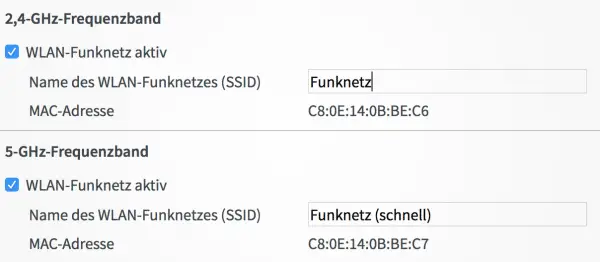 Assign different names . It is best to keep the name of the 2.4 GHz network and only rename the 5 GHz network. This ensures that you do not have to reconnect all wireless devices. However, the name doesn't matter, you just need to be able to tell them apart. Then click on " Apply " again.
Assign different names . It is best to keep the name of the 2.4 GHz network and only rename the 5 GHz network. This ensures that you do not have to reconnect all wireless devices. However, the name doesn't matter, you just need to be able to tell them apart. Then click on " Apply " again. 5th step:
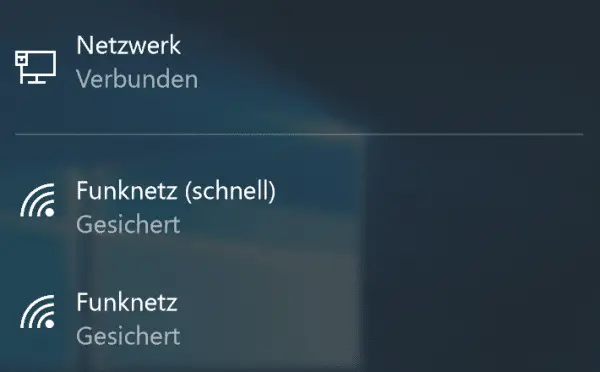 You will now find two WLANs in the WLAN list of your PC : The "original" and the 5 GHz WLAN with a new name. Both have the same password. Before the two ran in parallel, which is why you only saw one WLAN. Use one or the other WLAN depending on your needs and device. The rule of thumb: when it's slow, you have to switch to the other WiFi. This should make the connection significantly faster.
You will now find two WLANs in the WLAN list of your PC : The "original" and the 5 GHz WLAN with a new name. Both have the same password. Before the two ran in parallel, which is why you only saw one WLAN. Use one or the other WLAN depending on your needs and device. The rule of thumb: when it's slow, you have to switch to the other WiFi. This should make the connection significantly faster. What to do if it is not due to the WLAN?
WLAN is often, but not always, the cause of slow WLAN. If you are traveling slowly with an Ethernet cable, a typical suspect is the DNS server of the Internet provider: Here providers like to save, which means that websites are only accessed painfully slowly despite a fast connection.
1st step:
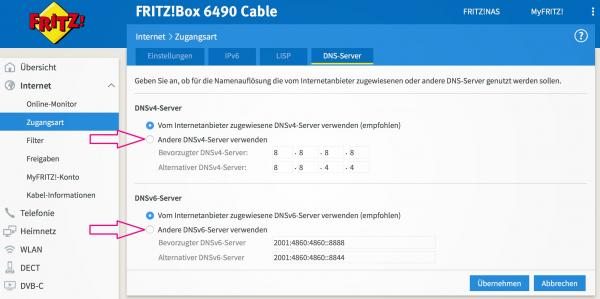 The DNS server mediates between the router and the Internet and resolves domain names such as heise.de into the IP addresses that the Internet normally uses. As a result, a faster DNS server can optimize the connection. To make changes, call up the point " Internet -> Access type -> DNS server " in the router interface . Set the item “ Use other DNSvX servers ” for both “ DNSv4 server ” and “ DNSv6 server ”.
The DNS server mediates between the router and the Internet and resolves domain names such as heise.de into the IP addresses that the Internet normally uses. As a result, a faster DNS server can optimize the connection. To make changes, call up the point " Internet -> Access type -> DNS server " in the router interface . Set the item “ Use other DNSvX servers ” for both “ DNSv4 server ” and “ DNSv6 server ”. 2nd step:
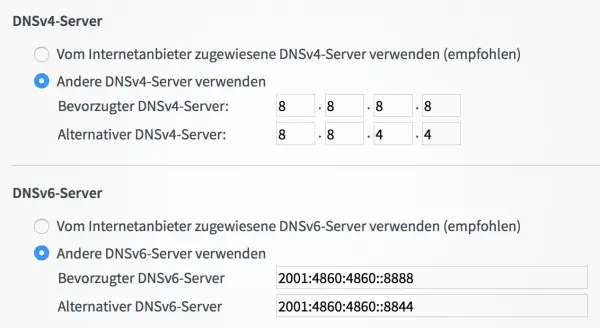 You now need the addresses of an alternative DNS service . The one from Google is popular ( https://developers.google.com/speed/public-dns/ ), but there are other alternatives such as OpenDNS ( https://use.opendns.com ). Enter the addresses. Click on “ Apply ”: The Internet should then work much faster. If this is not the case, you can still try another DNS server.
You now need the addresses of an alternative DNS service . The one from Google is popular ( https://developers.google.com/speed/public-dns/ ), but there are other alternatives such as OpenDNS ( https://use.opendns.com ). Enter the addresses. Click on “ Apply ”: The Internet should then work much faster. If this is not the case, you can still try another DNS server. What to do if it wasn't
If this does not bring any improvement and the WLAN optimization should not have helped either, the problem is most likely with the provider. In this case you should contact him and tell him that the internet connection is still slow despite optimization. Perhaps your connection is simply not properly switched or there are causes for which a technician has to be called out.