If you want to troubleshoot cache fullness issues or other internet connectivity issues, then you might need to clear the DNS cache on your Mac. Follow this how-to guide to easily clearing macOS's DNS cache, and feel free to share your comments in the comments section at the bottom of this page!
If you are the administrator of a network, a web developer, or the system administrator of a Mac, then you might need to clear macOS's DNS cache for several reasons. In particular, if you want to resolve a server name correctly or want to change your Mac's DNS address so that it can be detected by your individual system..
In addition to the reasons mentioned above, if you have edited the / etc / hosts file and need the changes to take effect without restarting your Mac, then you may need to flush and reset the DNS caches.
The easiest method to clear caches on Mac
FonePaw MacMaster is a much simpler solution to clear DNS cache on any version of Mac. It is is an application designed to clean, optimize and maintain your Mac, as well as to clear the caches of all its features..
Download and install the software on your Mac - you can get it for free by clicking here.
Free try
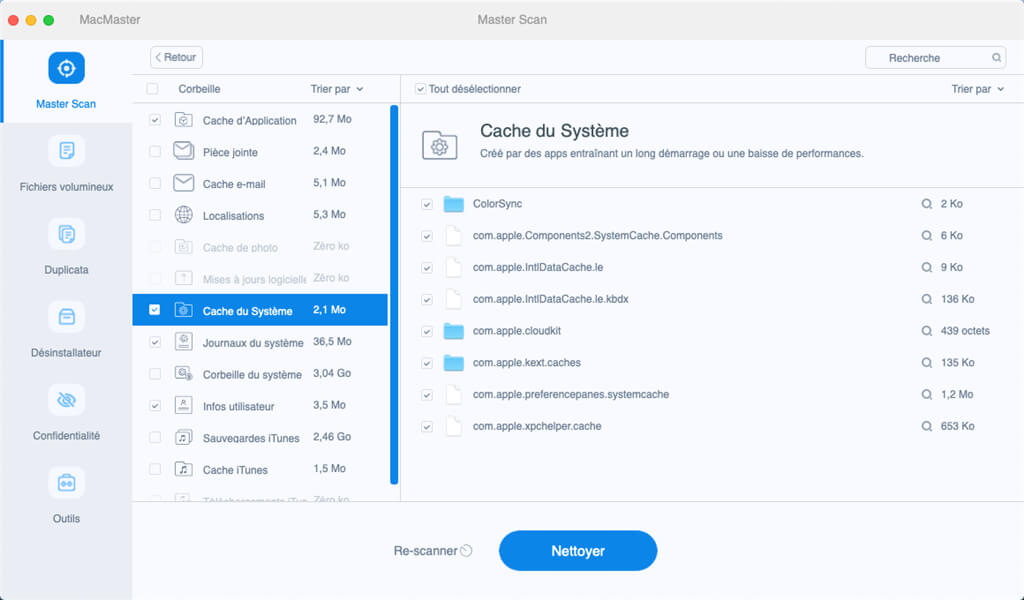
1. Start MacMaster..
2. Select “Macster Scan”, then run the scan.
3. Choose the caches you want to clear, and click “Clean”.
How to Clear DNS Cache on Mac
- The way to reset DNS cache is not the same on every version of Mac OS X. If you have been using Mac computer for a long time, then you might know that this process on OS X Yosemite is similar to some older versions. of macOS. This is probably due to the replacement of mDNSResponder by discoveryd, which then passed back to mDNSResponder.
- Despite this change, clearing the DNS cache is still done through a command in Terminal on Yosemite, but there are small differences depending on the exact version of OS you are using.
- You can dump Unicast DNS or Multicast DNS, or both. If you want to reset all DNS caches on your Mac, then you might need to flush both.
Clear DNS cache on macOS Sierra or macOS High Sierra
To clear the DNS cache on macOS Sierra and macOS High Sierra, you will need to use a new command. Read this quick guide to learn how to do it.
Clear DNS cache on Mac OS X Yosemite or El Capitan
Starting with OS X 10.10.4 and higher, version 10.11 included, Apple has discontinued discoveryd and replaced it with mDNSResponder. Therefore, to flush DNS caches on OS X Yosemite and Mac OS X El Capitan, as well as later versions, please use the following command:
sudo dscacheutil -flushcache; sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder; say cache flushed
The above command will clear all DNS caches on OS X 10.10.4 and later.
Older Mac users may notice that this command string matches the one used in the version of macOS that preceded Yosemite. However, versions of OS X Yosemite earlier than 10.10.4 will use a different command string as shown below.
To reset the cache, you must use the terminal. Find the Terminal app in / Applications / Utilities / or open it from Spotlight. Target both UDNS (Unicast DNS) and MDNS (Multicast DNS) with two different commands to completely flush all DNS caches on the most recent version of OS X.
Clear MDNS cache
- OS X Yosemite and later: sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder
- From OS X 10.10 to 10.10.3: sudo discoveryutil mdnsflushcache
Press the "Return" key and enter the administrator password when prompted.
Clear UDNS cache
sudo discoveryutil udnsflushcaches
Press the "Return" key again and enter the administrator password when prompted. In the second command, the word "caches" is plural. This variation in syntax is small but crucial.
How to Flush and Reset All DNS Caches on OS X Yosemite
If you want, you can also link the two commands. The following command will send you a notification once the caches are cleared:
sudo discoveryutil mdnsflushcache; sudo discoveryutil udnsflushcaches; say flushed
There is no doubt that MDNS and UDNS caches are different, but you can understand that both commands are required for the functional DNS cache to be fully flushed on OS X Yosemite. If you don't want to clear just one of the DNS caches, then that's fine.
Since OS X Yosemite has got rid of mDNSResponder, you do not need to end the mDNSResponder process to refresh the DNS caches as was the case on previous versions of Mac OS X.
If you are using an older version of OS X such as Mavericks, Mountain Lion, or Lion, then the commands to flush DNS are different. Below you can find the terminal commands for earlier versions of Mac OS X.
How to Clear DNS Cache on OS X Mavericks, Mountain Lion, and Lion
The command below will help you reset DNS cache on OS X 10.9.5 and earlier versions of macOS:
sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder
If you are using Mac OS X Snow Leopard, then please use the following terminal command.
How to Clear DNS Cache on Mac OS X Snow Leopard
Just copy the command below to reset DNS cache on OS X 10.6 through 10.6.8:
sudo dscacheutil -flushcache
How to check DNS cache details on OS X El Capitan or Yosemite
If you want to know what is cached when you change DNS then you can use the following commands:
Get UDNS cache statistics
sudo discoveryutil udnscachestats
Additionally, you can retrieve multicast DNS cache details with the following command:
sudo discoveryutil mdnscachestats
The two commands mentioned above give information such as the number of cached DNS entries. You can also get an account details in the following way:
UDNS Cache Stats: Cached 1250 of 1900
If you run these commands before and after running the flushcache variations, you will find that they need to be reset on the cache to 0 entries, as shown below:
MDNS Cache Stats: lo0: Cached 6 of 7500
How to know if the changes have been made
Once the cache is cleared, if you want to confirm if the IP address or the server name has actually changed, then use the "dig" command with the following URL:
dig fonepaw.fr
dig and nslookup are quite similar, but the difference is that dig works better by including additional information. It provides details such as the defined DNS server used to access the domain, a timestamp, and the time of the query. All of this information is helpful in troubleshooting server name issues. If the query time in the result is slow then you need to use a tool named "namebench" to get a faster DNS server, usually OpenDNS or Google DNS.
That's it that's all !
Conclusion
Hope now clearing DNS cache will not be a problem for you anymore. If you have any further questions, feel free to ask them in the comments section below!